Finally, a needle-free solution can shield people against Zika. For years, protection against this disease has mainly been mosquito bite prevention. There has been no vaccine against it. This time. People exposed to large mosquito populations have a way to avoid the fatal Zika virus.
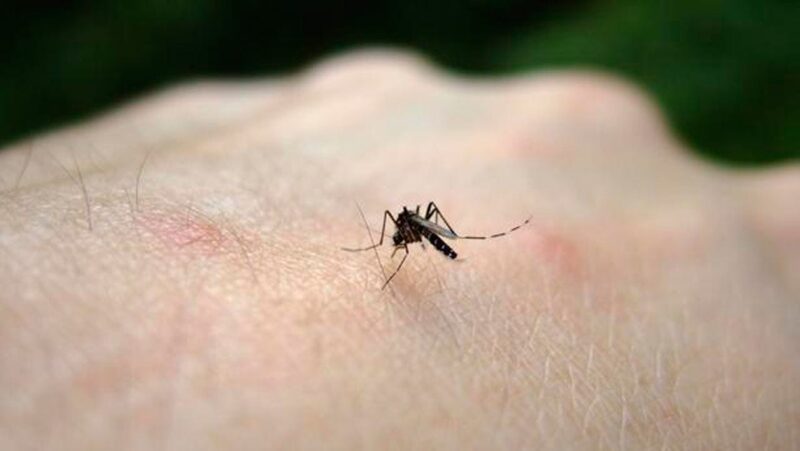

The Threat of Zika
This is a disease that hitches a ride on infected female mosquitoes. Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti are the carriers of this disease. They are often found in the Americas. Zika itself is mild. It fades on its own. But it impacts pregnant women and their developing fetuses. This disease continues to be a danger to people across South America, Central America, Africa, India, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific.
Traveling to places with active Zika cases will subject a pregnant woman to this disease. Once infected, this disease can go through the placenta and infect the developing fetus. That is why pregnant women must not travel to these areas. The CDC has a new list of countries affected by Zika. A non-pregnant woman who gets infected by Zika and shows symptoms, must not get pregnant right away. She must wait eight weeks to pass first. Checking with the ob-gyne can also help determine if the non-pregnant woman is safe to get pregnant.
The Needle-Free Vaccine
This new weapon against Zika is called the HD-MAP patch. It is effective and simple to administer. It is also pain-free and convenient to store. This needle-free solution is ideal for patients who do not like needles. The secret is the presence of thousands of micro projections.
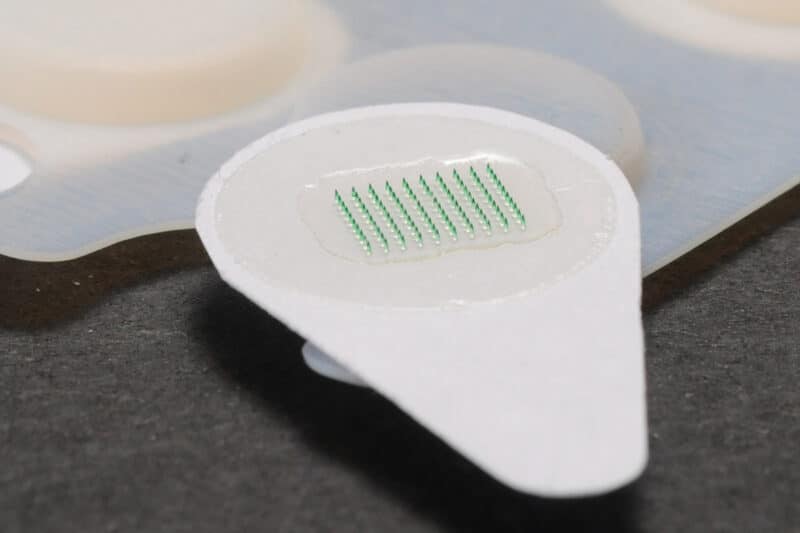

During the pre-clinical trial, the vaccine was able to protect against the live Zika virus. It targets NS1—a protein that is important for the survival of this virus. This vaccine patch stimulated the T-cells that increased by 270 percent than the responses from a syringe or needle vaccine.
Zika has been known to cause a mild disease. However, if a woman gets infected during pregnancy, it could lead to stillbirths or miscarriages. The baby could even be born with congenital conditions. Studies show that 89 countries are affected by Zika. But there are still no licensed vaccines for this illness.
The needle-free solution targets a protein inside the virus. It will not aggravate the symptoms of other mosquito-borne diseases like dengue in those who have been immunized. This particular target protein also helps in the replication of flaviviruses. This needle-free solution can then target other flaviviruses, such as Japanese encephalitis or dengue. It then provides a much greater protection than needle vaccines.
Another important feature of HD-MAP needle-free solution is its stability at high temperatures. Scientists discovered that the patch remained potent at 40 degrees Celsius for about four weeks. This stability increases the possibility of protecting the low- to middle-income communities in many areas where it is challenging to refrigerate.
Being Developed by Researchers
Researchers at the University of Adelaide in Australia. It triggered a significant immune response to Zika in experiments involving mice. According to the Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acid Journal, the needle-free solution uses a high-density microarray patch or HD-MAP patch that was developed by the University of Queensland.

Zika is a dreadful illness that affects mothers and their unborn children. It is relieving to know that there is an effective form of vaccine that can help defend your body from Zika. This vaccine patch will be able to change lives. It can bring healthy babies into the world again.