Serious mosquito-borne diseases, such as dengue and severe dengue can affect your quality of life. It may also lead to more complications or even death. These diseases are common in areas where mosquito populations are high. These places are often subtropical and tropical. Understanding the differences between these serious mosquito-borne diseases can help you protect yourself and your home.

Dengue Fever
This illness is from a mosquito that carries any of the four variants of DENV (dengue virus). It is common in the Pacific Islands, South America, Central America, Africa, and parts of Asia. Dengue is not a contagious illness. But it can transfer from the mother to the developing fetus during pregnancy. The first infection is often mild. But if you get infected with another variant, your symptoms will be more severe.
Some parts of the United States are also affected by dengue. People traveling to or living in these places have the highest risk. The elderly and children have weak immune systems. This makes them more likely to contract DENV. Studies show that about 400 million people get infected by serious mosquito-borne diseases like dengue each year. Most of the patients do not have symptoms.
Most patients do not have symptoms. If there are, high fever occurs with petechial rashes, vomiting, and nausea. Pain in the joint, muscle, and bone is also evident. These symptoms appear 4 to 10 days after the bite. They can last for about three to seven days. One in 20 patients will develop severe symptoms after the first symptoms begin to disappear.

Severe Dengue or Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
This is one of the many serious mosquito-borne diseases that have life-threatening symptoms. The warning signs will occur one to two days after the fever fades. Severe dengue can be fatal. This is a medical emergency that needs an immediate trip to the emergency room if the following symptoms occur:
- Blood in the stool
- Blood in the vomit
- Irritability
- Extreme tiredness
- Restlessness
- Frequent vomiting
- Bleeding gums
- Nose bleeds
- Abdominal or stomach pain
Patients with severe dengue need medical attention right away. Hospitalization is necessary for ideal medical care. This will also prevent possible death. Dengvaxia is a vaccine against dengue. It is approved for adolescents and children, 9 to 16 years old, who already had a previous dengue infection. They also live in areas where dengue is an endemic sickness. Less severe dengue symptoms may not need hospitalization. Managing the illness at home is enough.
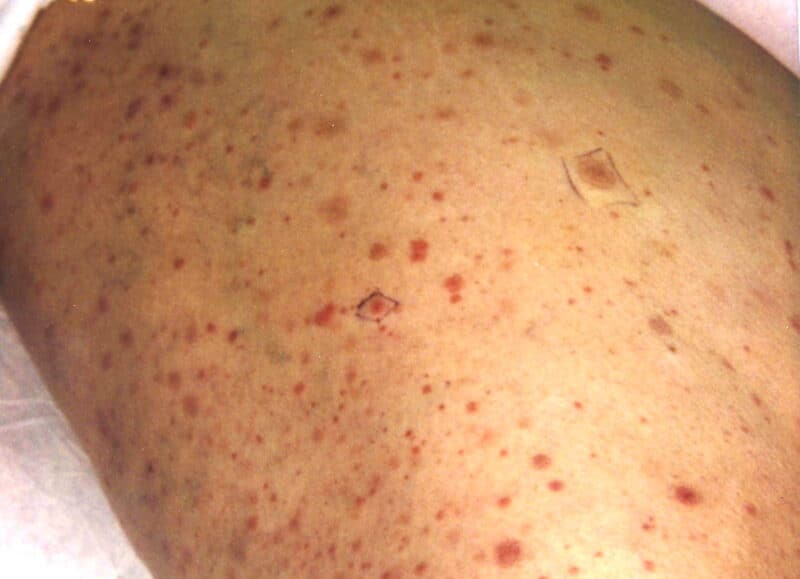
Main Causes of Dengue
Dengue fever and severe dengue are caused by any of the four strains. An infected mosquito bites you. The dengue virus enters your blood and replicates there. The virus and your immune system respond by making you sick. The virus destroys parts of the blood essential for providing structure to your blood vessels and forming clots. Your immune system then releases chemicals. The combined reactions to the virus can lead to blood leaking out of the blood vessels. This will then lead to internal bleeding.
Serious mosquito-borne diseases like dengue are spread by the bite of infected mosquitoes. For dengue, Aedes is the culprit. This mosquito can also carry viruses like chikungunya. When this species of mosquito bites an infected person and then the infected mosquito bites a healthy person, the healthy person gets infected with dengue. A pregnant woman with dengue can also transfer the virus to the developing fetus.
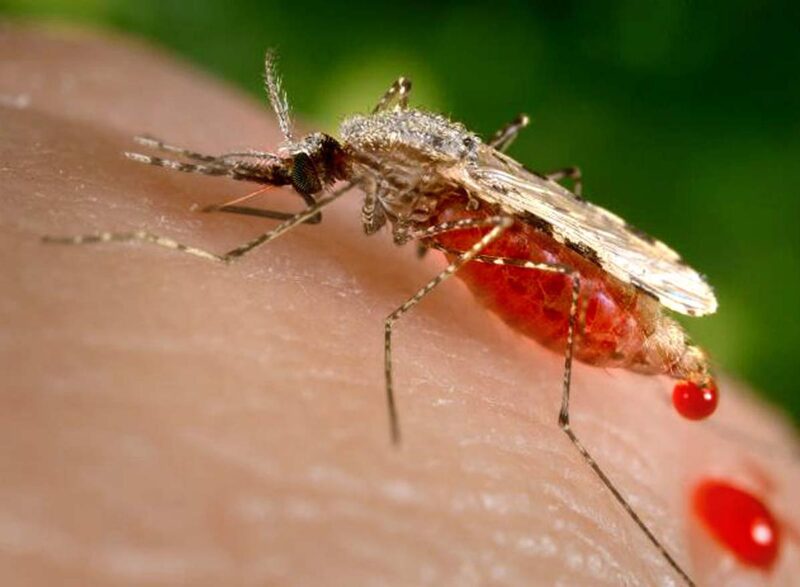
Managing Symptoms

The doctor will diagnose you by performing a blood test. A lab will test a sample of your blood through a vein in your arm. The lab will test it for signs of dengue. This may also determine which of the four variants you have. The doctor can also use your blood sample to detect other viruses that can cause similar symptoms. Unfortunately, there is no treatment for dengue fever. The doctor will provide many recommendations on symptom management. These recommendations will also be about when and if you should rush to the ER. Some of these recommendations are the following:
- Never take aspirin or ibuprofen because these medications can increase your risk of internal bleeding.
- Maintain hydration by drinking plenty of fluids.
- Treat pain with acetaminophen.
- Rest as much as you can.

Preventing serious mosquito-borne diseases is important in keeping the symptoms at bay. This includes using repellants, cleaning out the gutters, and pouring out stagnant water. Keeping the bites away can maintain your and your family’s health and well-being.