Have you ever tried to go boating?
Boating is a very enjoyable recreational activity. It is something you can do in the company of friends or family. You can easily take a boat on a lake or on an ocean to relax. Whatever you plan to do on your boating trip can be dampened easily by the appearance and the attack of flies and mosquitoes. When these parasites surround you, you cannot concentrate on whatever activity you want to have on board. It is always best to have bite-free skin when you go boating.
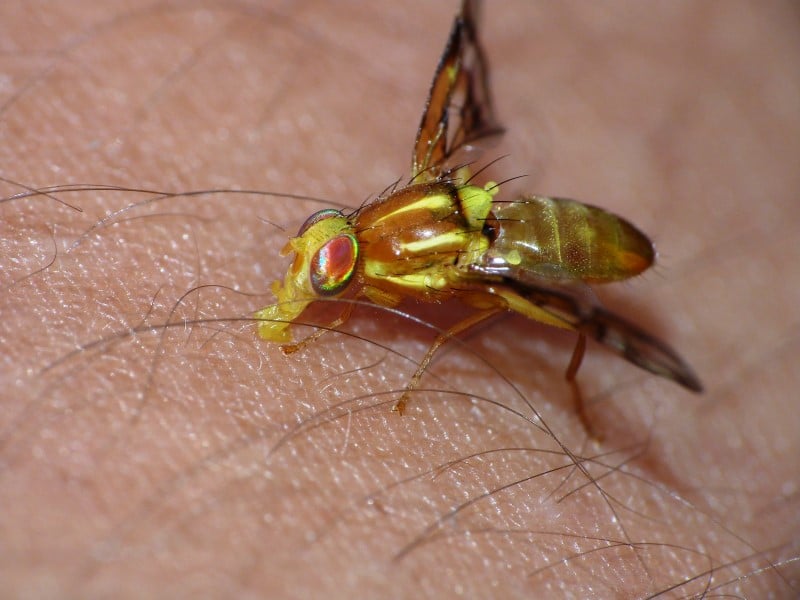

Biting flies, like any other parasite, constantly look for a reliable and substantial host. Many people have experienced the bite of a type of biting fly at one point or another. There are several types of biting flies, but mosquitoes are still responsible for most of the bite cases. To know how to repel biting flies, you should know more about them.
A fly is a winged insect that has two wings. It is different from most winged insects that generally have four wings. The fly that we see around trash bins is the fly with sucking mouthparts. Biting flies have piercing mouthparts that bite humans or other animals. Biting flies are like mosquitoes in a sense that they locate animals and humans by sensing the moisture and the carbon dioxide in their breath. They are also attracted to perspiration, warmth, movement, and dark colors. Once they find the right host, biting flies insert their piercing and lacerating mouth parts into the skin. They inject their saliva, which contains anticoagulants that prevent blood from clotting as they feed. Sensitive humans usually have extreme allergic reactions to the saliva.
Like mosquitoes, biting flies are also vectors of debilitating and deadly diseases to humans on a global scale. Here are the various species of biting flies and the diseases they carry:
- Psychodidae (“Sand Flies”). Carry bartonellosis, leischmaniasis, and sand fly fever
- Chrysops discalis (species of “Deer Flies”). Carry tularemia
- Ceratopogonidae (“Biting Midges”). Carry a variety of pathogens including the blue tongue virus
- Simuliidae (“Black Flies”), Stomoxis calcitrans (“Stable Flies”), and Tabanidae (“Horse Flies”). Cause allergic reactions.
Know Your Biting Flies
Below are the known biting flies that prey on humans and animals:
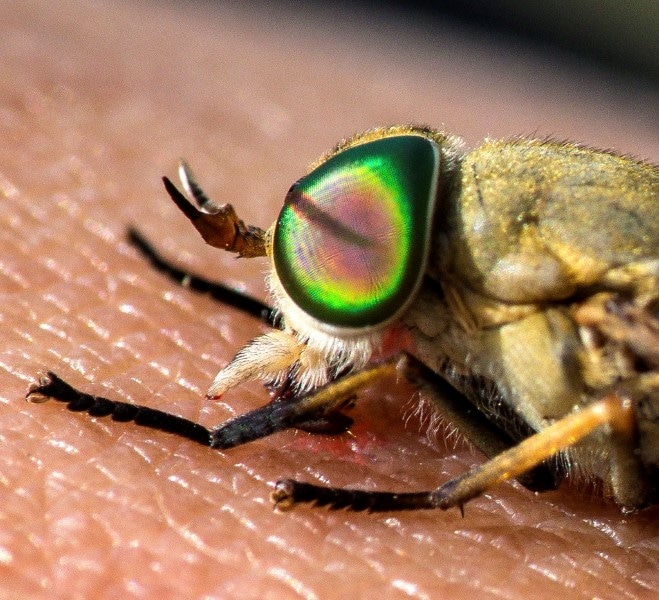
1.Family Tabanidae. This classification includes horse flies and deer flies. Deer flies transmit diseases to humans in the United States. Rabbit fever or tularemia is a known bacterial infection that can be contracted from contact with infected animals or contaminated objects; tick bites, and the deer fly species known as Chrysops discalis. You can encounter deer flies during the spring season. They are about a quarter of an inch long and medium-sized. It is about the size of an ordinary housefly. They are yellowish brown to black in color. Their wings have dark bands. Horse flies and deer flies have iridescent green eyes.
During their immature, maggot-like life stage, deer flies are aquatic. You can find the adult deer flies along swamps, streams, marshes, lakes, and ponds. They are considered annoying, since they are fond of buzzing around people’s heads. When many them are present, the buzz around you all at the same time. Horse flies and deer flies have scissor-like mouthparts that cut into your skin when they bite. The tiny cut allows the blood to flow freely. The flies them lap the blood up. Bites can be very painful because they are made so crudely.
Horse flies are completely black in color. They are also known as greenheads, which have green eyes and light brown bodies. Horse flies are fast and strong fliers that feed actively on the blood of animals such as livestock or pets. Horse fly larvae also live in water or any location that is moist. In their aquatic environment, the larvae prey on insects. Then, they grow bigger and move toward dry soil to go through their cocoon or pupal stage. The horse fly life cycle may take about two years to come full circle.
2.Family Stomoxys calcitrans. This classification includes stable flies. Stable flies are about a quarter inch long with four distinctive dark striped on the thorax, behind their head. They resemble house flies, but they have pointed mouthparts or proboscis under its head. This part of their mouth sucks the blood, just like a mosquito would. Stable flies are usually abundant during the fall and summer seasons. They are they are willing and able to fly long distances to bite humans, livestock, and pets.
Stable flies usually bite the ankles, inflicting a stabbing, nagging, pain. They are active during the morning and in the late afternoon. Stable flies lay their eggs in piles of rotting plant matter such as glass clippings, sea grass, manure, and haystacks. Stable flies are almost identical to house fly larvae.
3.Family Simuliidae. This is the family of black flies. Adult black flies are about an eighth of an inch in length with broad wings. They appear to be humpbacked. Black flies also like moist environments. They are also known as buffalo gnats. They are usually found near rivers and creeks where the black fly larvae cling to the submerged rocks.
Adult black flies can fly as far as ten miles just to search for food. Fortunately, black flies do not carry diseases to humans. When black flies are present in large numbers, black fly bites can be life threatening. They are usually in large numbers during early summer and late spring. Reported deaths are usually from blood loss and allergic reactions from their bites. It can also be fatal when you inhale the flies. Black flies cause bleeding and swelling. The bites are also slow to heal and vey itchy. Black flies prefer to attack areas of your body where clothes fit you tightly. They also like to attack the head.
4.Family Ceratopogonidae. Biting midges belong to this family. Remember that these midges are different from the midges belonging to family Chironomidae, which are like mosquitoes, but they just don’t bite. Biting midges are about 1/32 inch in length. Also, known as gnats, punkies, or no-see-ums, biting midges can go through the door screens and window screens. They are treated as serious pests along rivers, oceans, lakes, and ponds. They bite, night or day.
The larvae of these biting midges live and thrive in rotting vegetation, moist soil, tree soil, moist sand, and other damp areas at the edges of lagoons, ponds, and marshes. Several biting midges species suck the blood of insects, like mosquitoes. Other species suck human blood.
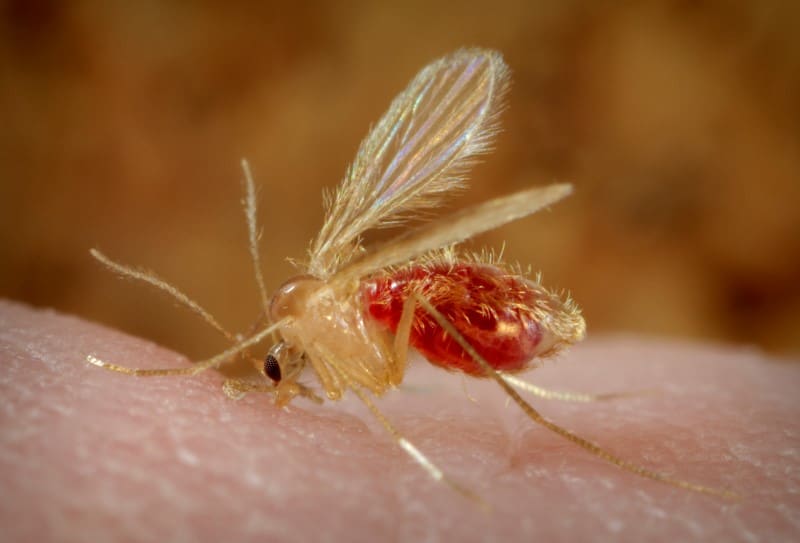
5.Famil Pschodidae. This is the family of sand flies. Sand flies are related to drain flies, which do not bite. Sand fly larvae are worm-like and tiny. The larvae live in decaying, vegetation, water, moss, or mud. Adult sand flies do not exceed an eighth of an inch long. They have long legs, colored brown or gray, hairy, and their wings for the shape of a “V” when they are resting.
Most species of sand flies feed on reptiles, amphibians (at night), and mammals. Many areas of the world, which include south of Texas in the U.S., have sand flies that are suspected to transmit leischmaniasis, which is a disfiguring disease in humans, caused by protozoa. The sand fly species referred to here is the Lutzomyia.
How to Manage Biting Flies
If you’re boating, or if you’re on vacation somewhere, how do you manage biting flies? Control of biting flies in a large area can be difficult because the larvae are tucked away in hidden places. Another reason is that adult biting flies fly a long way from where they thrived as larvae. Below are some known methods in managing biting flies:
Sanitize. This is an important method in controlling biting flies. If you get rid of decaying vegetation and manure, you eliminate the place where the larvae of biting flies thrive. By getting rid of the substances that support their larval development, you stop the proliferation of adult biting flies.
Exclude. This is also an effective way to prevent biting flies from entering your living space, whether you’re at home or in your boat. Your windows and doors should have screens that have a finer mesh than the standard screens. Fly paper does not attract biting flies. Warm blooded animals do. Use fans to keep small rooms fly-free. Torches and burning candles produce smoke that help ward off these flies.
Eliminate. This method is limited in the control of biting flies. ULV (ultra-low volume) treatments and space sprays, using non-residual pesticides, are the best choice for small areas.

Managing Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are always around when there is stagnant water and perfect hosts. Your boat is the ideal nursery for mosquitoes. In hidden nooks and crannies, there is water kept from previous voyages or even rain. You should always make sure that you protect yourself from these small predators or you would end up with diseases such as Zika, Dengue, and Malaria. To manage these insects, you should keep your living space screened off and always wear long pants and long sleeved shirts, especially during dusk and dawn. It also helps to have insect sprays and mosquito coils in stock. Citronella candles and mosquito nets also work.
Many types of anti-mosquito devices, creams, and sprays are available in the market. It is better to stick to natural or organic repellents so that you don’t suffer from the side effects of strong, synthetic repellents such as DEET. According to the Center for Disease Control, repellents that contain oil of lemon eucalyptus and picaridin have lasting protection.
You can actually make your own repellents using ten drops or more of any essential oil that repels insects and mixing it in distilled water.

Keeping Bugs Away While Boating
As you know, bugs are everywhere. More of them tend to appear in warm climates, where boating is a regular activity. You may be on your boat, but bugs have their way of making it aboard from the port or from the water itself. Below are some of the natural ways to keep bugs away from your boating trip:
- Keep everything tidy and clean. Cleanliness is imperative on every boat. In places with warm climate, crumbs signal every bug within a hundred miles. It is best to always get rid of bits of food on the floor and on the table. Spilling something is common on the boat. Just clean it up immediately. After cooking, clean the stovetop as well. Cleaning your galley should be done regularly and thoroughly.
- Use repellents with natural ingredients. Keeping organic repellents like BugMace (cruelty-free, vegan, certified with PETA, and number one repellent on Amazon) is always beneficial. You can also use essential oils such as basil, lavender, vetiver, pine, bergamot, thyme, peppermint, tea tree, lemon eucalyptus, and eucalyptus. The flies and mosquitoes that usually pester you on the boat don’t stand a chance at all with these natural repellents.
- Use vinegar. One species of flies you should also be aware of is fruit flies. Perhaps you notice that they just pop out of nowhere one by one. Minutes later, they are all congregating over your sink, dining table, or snack box. Place small bowls of apple cider vinegar with a few drops of dish soap, on surfaces where food is located. Do this, so that you can eat without worrying about swallowing a fruit fly by accident.
- Always close windows and doors at night and at dawn. Mosquitoes and biting flies have these two periods of the day to actively bite you and feed on your blood. Prevent them from getting to you or to your loved ones on the boat by just closing he doors and windows.
Boating is an enjoyable activity that allows you to commune with nature. Surrounded by the ocean, you do not need to worry about insects such as biting flies or mosquitoes ruining your adventure. It is best to be fully prepare yourself and your family. It is not good to assume that no insect will bite you when you leave the port. Remember, they are everywhere and you are one of their food sources. Keep these insects away while boating, so you can have the time of your life.